Google Search Console (previously Google Webmaster Tools) is a free service by Google that allows you to check your website's indexing status and to optimize its visibility for searchers. Search Appearance Structured Data This is where you can see whether Google finds any structured data on your website (including manual highlights from Data Highlighter, which we'll be looking at more closely later on). I do recommend using it, even if you have structured data on your website, especially in the case of new sites. Example: The same page when you check it for being indexed: HTML Improvements Here's what you should see ideally in this section: However, if you have some on-page SEO issues, you will see those. If you want to get ranked, say, for marketing, but have nothing associated with that in your top 20 keywords, you'll have hard times in trying to move your site to the top. The same goes for your other pages that are not indexed: Check them here. There may also be a case when you don't want one of your pages to be visible through search. But errors can reflect real problems on your website. If that's the case, delete those by marking errors as fixed and adding the resources that provide those links to your disavow file. If you had some indexing problems, then fixed the issues; you may also resubmit your sitemap.

Google Search Console (previously Google Webmaster Tools) is a free service by Google that allows you to check your website’s indexing status and to optimize its visibility for searchers.
To adjust your website in Google Search Console, you need to go to the dashboard and select your site’s main property. If it’s www, then select that choice. If you have an SSL certificate, you’ll have to select the property with “https” (with or without www—depending on your main mirror).
Search Appearance
Structured Data
This is where you can see whether Google finds any structured data on your website (including manual highlights from Data Highlighter, which we’ll be looking at more closely later on). If there are any errors, there will be a notification that looks like this:
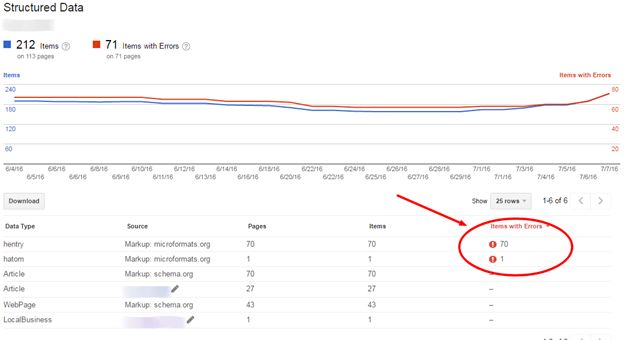
Microformats with errors don’t work, so it’s better either to either remove them or to fix the issue. If schema.org is already implemented correctly for your site, you can just remove those formats with errors. Good markup will help search engines to better understand the contents of your webpages. There’s no direct evidence that those may improve your rankings, but rich snippets designed wisely (not for the sake of appearance) influence the user experience (UX); user behavior, in turn, implicitly affects rankings.
Rich Cards
These are, again, part of structured data. You should definitely use rich cards if your website provides one of these types of information:
- Recipes
- Events
- Products
- Reviews
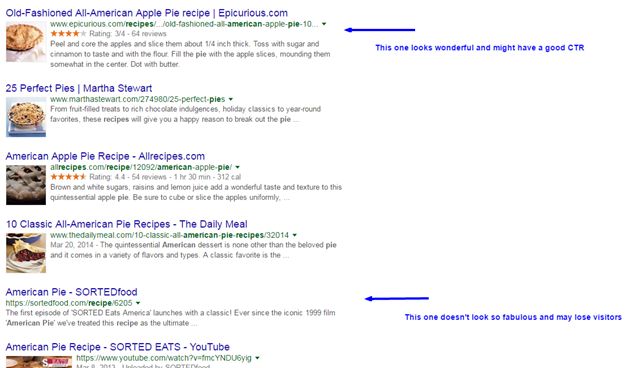
Your snippet in search will look fantastic, for example in the case of recipe pages, where images are allowed.
Sometimes, you have certain limitations and cannot modify your website to input microdata. You should use Data Highlighter then. It’s very easy to use and Google has detailed instructions for it. It allows you to mark similar pages in a group one at a time. I do recommend using it, even if you have structured data on your website, especially in the case of new sites. Sometimes it helps to find out whether some pages that you thought had been indexed are in fact not indexed.
Example:
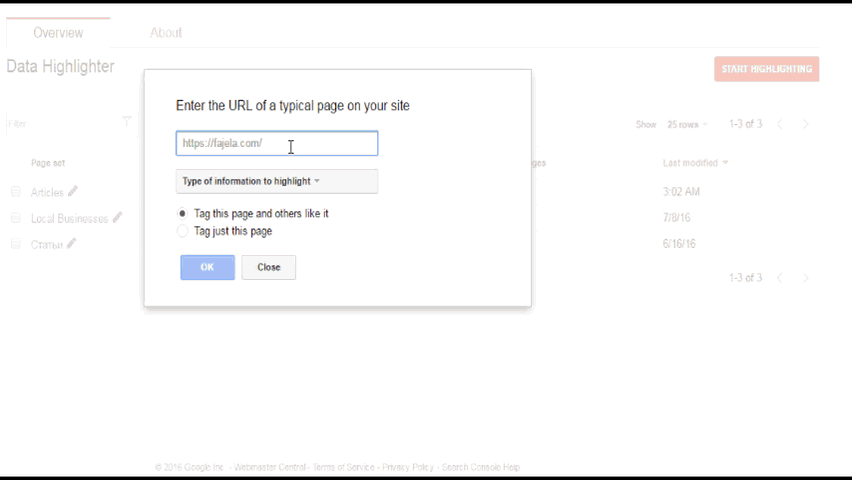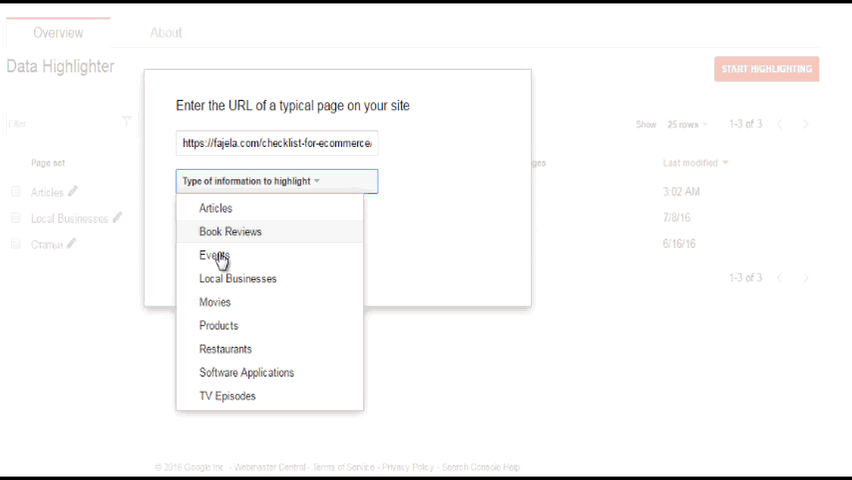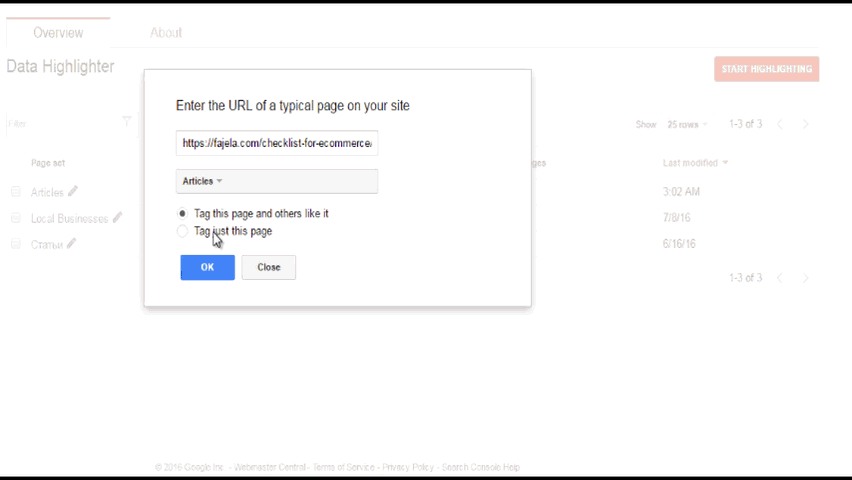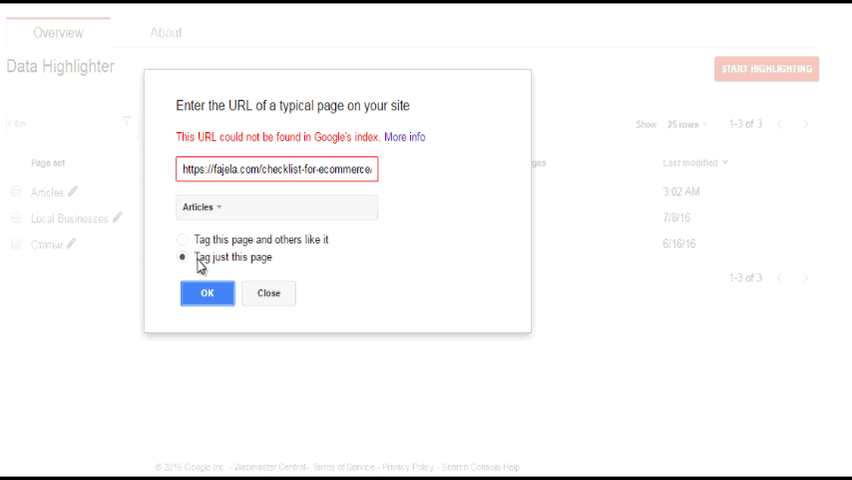
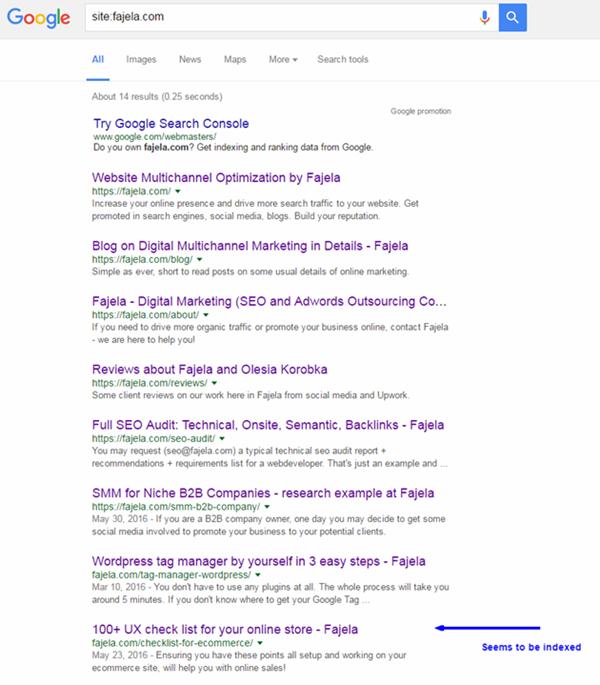
Here’s what you should see ideally in this section:

- Title tags
- Meta description
- Non-indexable content
- The problems with those may be as follows:
- Missing tags
- Duplicates
- Long tags
- Short tags
- Non-informative
I recommend you deal with those even for the pages that are not promoted.
Sitelinks
This section is usually used in two cases.
The first is when you want to demote the link from search. For example, if you have two pages ranked for the same keyword and the one you are promoting is ranked lower in search, then you may want to demote the other one.
Otherwise, you may want to polish your branding search results.
There are also Accelerated Mobile Pages in the Search Appearance section. We won’t look at those in detail here, because that can be another very long article.
Search Traffic
Search Analytics
This is much more convenient to look at in your Google Analytics account; however, there’s a lot of marketing data here as well. And it’s another, indirect method to see whether your page is indexed; if there are no visitors from search, and it’s not even mentioned there, then it’s highly probable that it’s not indexed.
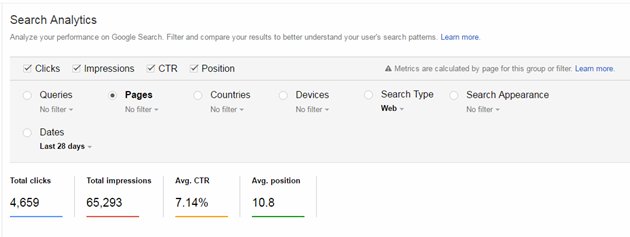
You may also analyze some actual queries, pages, countries, etc. (see image, below). It is also very helpful for analyzing how many image or video clicks you get from search (filter > Search Type > Image/Video). And here you can estimate the clicks on your pages in search that were shown with optimized snippets. In this case, it seems worth it:
COMMENTS